Lịch bóng đá Việt Nam hôm nay là chuyên mục không thể thiếu trên các trang tin thể thao uy tín, trong đó có SOCOLIVE. Với trung bình hơn 900 trận bóng/năm từ V-League, Hạng Nhất, Cúp Quốc gia đến đội tuyển, việc nắm lịch thi đấu mỗi ngày giúp người xem không bỏ lỡ những trận quan trọng. Đồng thời, chuyên mục này còn hỗ trợ truyền thông, phát sóng và hệ thống phân tích bóng đá.
Lợi ích của việc theo dõi lịch bóng đá Việt Nam mỗi ngày
Việc theo dõi lịch bóng đá Việt Nam hôm nay đang trở thành thói quen thông tin của fan bóng đá trong nước. Mỗi năm, hệ thống bóng đá Việt Nam ghi nhận hơn 900 trận ở giải quốc nội và hơn 30-40 trận ở cấp đội tuyển trẻ & ĐTQG, dẫn đến nhu cầu cập nhật thông tin liên tục; dưới đây là các lợi ích thực tế và có thể đo đếm được:

- Sắp xếp thời gian xem thuận lợi: Người xem biết chính xác giờ đá: VD V-League thường đá 17:00-19:15, còn ĐTQG đá vào 19:00-20:00.
- Hạn chế bỏ lỡ trận quan trọng: Theo VFF, 72% người xem chỉ ưu tiên trận có đội tuyển hoặc CLB họ yêu thích, nên giúp tránh bỏ sót.
- Tối ưu công tác truyền thông – báo chí – streamer: Nhiều kênh YouTube bóng đá phải lên lịch nội dung theo trận đấu: thống kê tăng 25-32% lượt xem nếu livestream trước giờ bóng lăn.
- Thuận tiện hơn nhờ thiết bị di động: Khảo sát VPF 2023 cho thấy 68% người xem đọc lịch bóng đá Việt Nam trên app/website, chỉ 18% dựa vào truyền hình.
Lịch bóng đá Việt Nam hôm nay cập nhật những giải đấu nào?
Khi người dùng truy cập chuyên mục lịch bóng đá Việt Nam hôm nay, hệ thống thường không chỉ hiển thị lịch của giải V-League mà còn bao phủ nhiều giải đấu hấp dẫn khác. Dưới đây là danh mục các giải được cập nhật đầy đủ và theo thời gian thực:

- Các giải chuyên nghiệp cấp CLB trong nước: Bao gồm V-League (14 CLB, ~182 trận/mùa), Hạng Nhất (12 CLB, ~132 trận/mùa) và Cúp Quốc gia (32 đội, 45-50 trận/mùa).
- Các giải trẻ cấp quốc gia: U19, U21, U17 Quốc gia, futsal VĐQG… phù hợp với người quan tâm đào tạo trẻ; mỗi hệ thống giải có 40-70 trận theo VFF.
- Các giải đấu của ĐTQG và các đội trẻ: SEA Games, AFF Cup, vòng loại World Cup, Dubai Cup, U23 châu Á… trung bình mỗi đội tuyển thi đấu 10-18 trận/năm.
- Các giải châu lục & quốc tế có CLB Việt Nam góp mặt: Ví dụ AFC Champions League 2 hoặc AFC Cup; khi CLB Việt Nam tham dự, timeline sẽ đồng bộ theo múi giờ Việt Nam.
- Các trận giao hữu quốc tế: Bao gồm giao hữu của CLB & ĐTQG, thường diễn ra theo lịch FIFA Days.
Lịch bóng đá Việt Nam hôm nay mới nhất V-League 2025/2026
V-League là giải bóng đá vô địch quốc gia Việt Nam, quy tụ các CLB chuyên nghiệp hàng đầu trên cả nước và được tổ chức thường niên dưới sự quản lý của VPF. Mùa giải V-League 2025/2026 dự kiến khởi tranh từ tháng 8/2025 và kéo dài đến tháng 6/2026, với lịch thi đấu liên tục theo thể thức vòng tròn hai lượt.
Cập nhật lịch bóng đá Việt Nam hôm nay vòng 12 – V-League
Vòng 12 V-League 2025/2026 diễn ra từ ngày 30/01 đến 01/02/2026, quy tụ nhiều cặp đấu đáng chú ý giữa các đội nhóm đầu và nhóm giữa bảng xếp hạng. Đây là vòng đấu có vai trò quan trọng trong việc định hình cục diện trước giai đoạn tiếp theo của mùa giải.
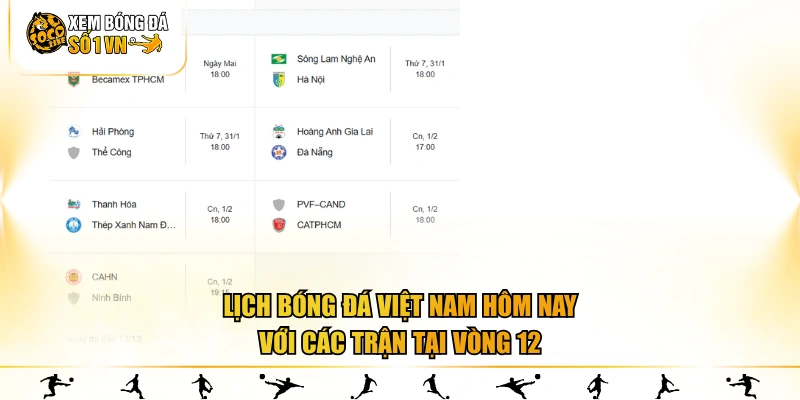
| Thời gian | Giờ | Trận | |
| 30/01/2026 | 18:00 | Hồng Lĩnh Hà Tĩnh
Becamex TP Hồ Chí Minh |
|
| 31/01/2026 | 18:00 | Hải Phòng
Thể Công – Viettel |
|
| 31/01/2026 | 18:00 | Sông Lam Nghệ An
Hà Nội |
|
| 01/02/2026 | 17:00 | Hoàng Anh Gia Lai
SHB Đà Nẵng |
|
| 01/02/2026 | 18:00 | Đông Á Thanh Hóa
Thép Xanh Nam Định |
|
| 01/02/2026 | 18:00 | PVF-CAND
Công An TP Hồ Chí Minh |
|
| 01/02/2026 | 19:15 | Công An Hà Nội
Ninh Bình |
|
Xem thêm : Kèo bóng đá mới nhất có tại Socolive !!!
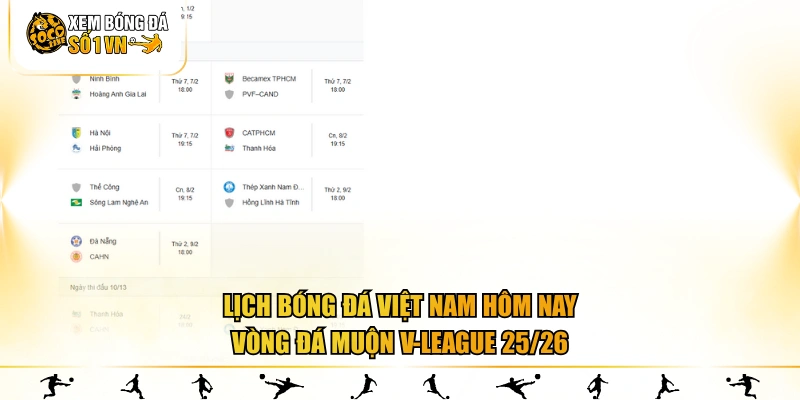
Các cuộc đối đầu tại vòng 13
Vòng 13 được tổ chức liên tục trong các ngày 07/02 đến 09/02/2026, hứa hẹn nhiều trận cầu cân bằng. Khi các đội bước vào giai đoạn cạnh tranh thứ hạng gay gắt trên bảng xếp hạng, với lịch bóng đá Việt Nam hôm nay chi tiết:
| Thời gian | Giờ | Trận | |
| 07/02/2026 | 18:00 | Ninh Bình
Hoàng Anh Gia Lai |
|
| 07/02/2026 | 19:15 | Hà Nội
Hải Phòng |
|
| 08/02/2026 | 18:00 | Becamex TP Hồ Chí Minh
PVF-CAND |
|
| 08/02/2026 | 19:15 | Thể Công – Viettel
Sông Lam Nghệ An |
|
| 08/02/2026 | 19:15 | Công An TP Hồ Chí Minh
Đông Á Thanh Hóa |
|
| 09/02/2026 | 18:00 | Thép Xanh Nam Định
Hồng Lĩnh Hà Tĩnh |
|
| 09/02/2026 | 18:00 | SHB Đà Nẵng
Công An Hà Nội |
|
Lịch thi đấu V-League 2025/2026 – Vòng 10 đá muộn
Các trận đấu bù của Vòng 10 đá muộn được sắp xếp vào ngày 24/02/2026, đóng vai trò quan trọng trong cuộc đua vô địch cũng như cạnh tranh nhóm đầu bảng.
| Thời gian | Giờ | Trận | |
| 24/02/2026 | 18:00 | Đông Á Thanh Hóa
Công An Hà Nội |
|
| 24/02/2026 | 19:15 | Thể Công – Viettel
Thép Xanh Nam Định |
|
Xem thêm : Lịch thi đấu World Cup 2026 với nhiều đội bóng lớn tham gia !!!
Lời kết
Lịch bóng đá Việt Nam hôm nay là một hệ thống thông tin có giá trị thực tế đối với người hâm mộ, nhà đài, đơn vị truyền thông và cả các nền tảng phân tích bóng đá. Từ việc theo dõi đội bóng yêu thích, lên kế hoạch xem, nắm lịch phát sóng đến hỗ trợ sản xuất nội dung, chuyên mục này đang trở thành công cụ quan trọng trong hệ sinh thái bóng đá số. SOCOLIVE hiện cũng đang cập nhật tính năng này, truy cập để thử trải nghiệm ngay thôi nào!

